Learning tips for Azure Fundamentals certification AZ-900
Learning tips for Azure Fundamentals certification AZ-900

Cet article contient les éléments techniques essentiels pour pouvoir passer la certification Azure AZ-900.
Vous trouverez aussi des formations sur Youtube:
Et aussi des exemples d’examen bien pratique pour réviser:
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/certifications/resources/az-900-sample-questions https://learn.microsoft.com/fr-fr/certifications/exams/az-900/practice/assessment?assessment-type=practice&assessmentId=23
- https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=az-900+exam+questions
Le cours officiel de Azure sur cette certification est divisé en 3 thèmes appelées des Learning Path:
- Cloud concepts
- Azure compute and networking services
- Describe Azure management and governance
Voici des tips sur ces 3 thèmes à partir de la formation que j’ai pu suivre et des exercices passés pour préparer la certification.
1 Learning Path: Cloud concepts
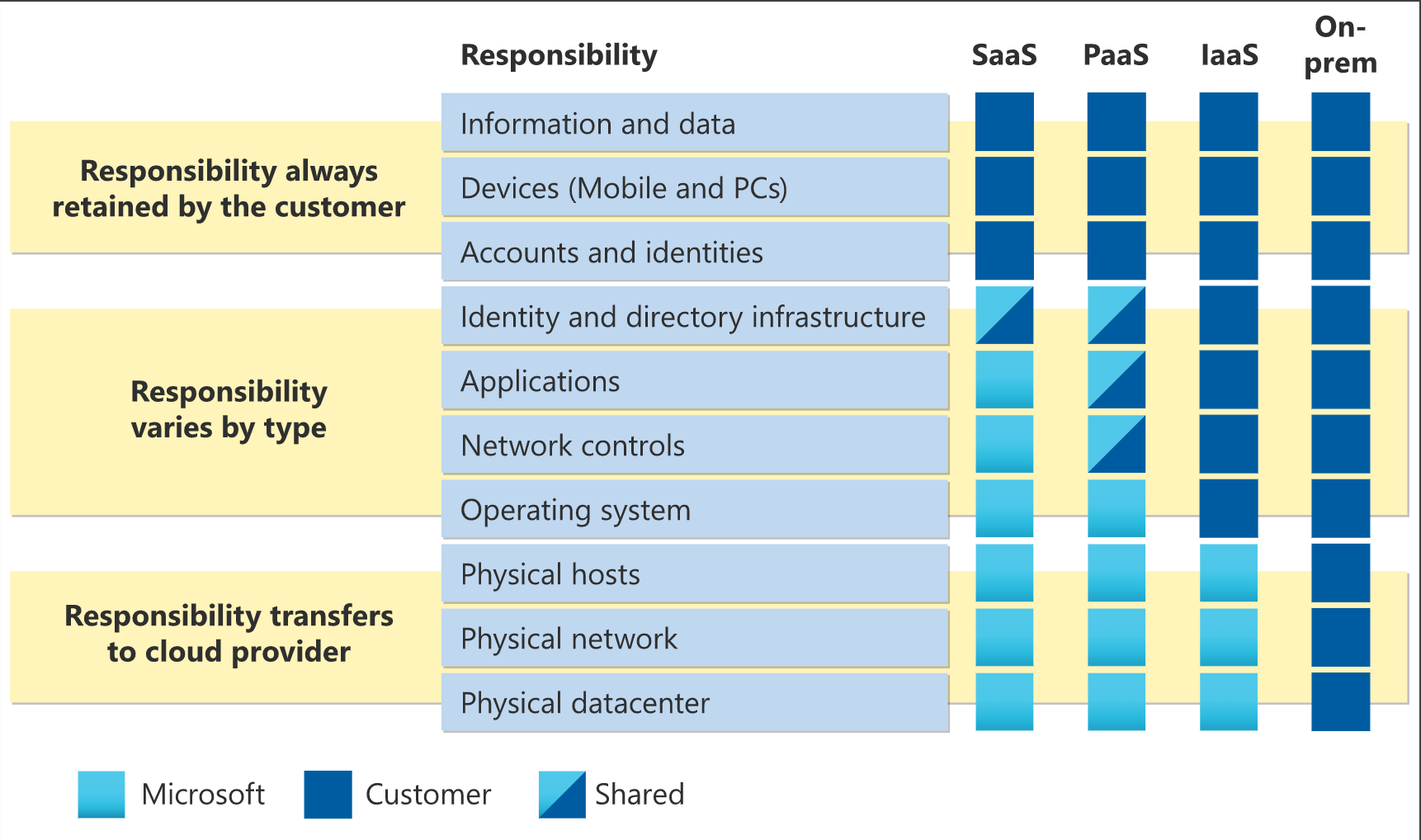
Shared responsibility model
- Consumer responsible at least of data, devices and accounts
- Cloud providers of physical datacenter, network, hosts…
Cloud models
- Private cloud: own datacenter
- Public cloud: use cloud provider
- Hybrid: mix of private and public
- Multi-cloud: use multiple cloud providers
A hybrid cloud is a computing environment that combines a public cloud and a private cloud by allowing data and applications to be shared between them.
Discuss different types of cloud models - Training | Microsoft Learn
Azure Arc: to manage cloud models
Azure Vmware: run Vmware workload on Azure
Cloud public
- Aucune dépense en capital pour effectuer un scale-up.
- Les applications peuvent être rapidement configurées et déprovisionnées.
- Les organisations paient uniquement pour ce qu’ils utilisent.
Cloud privé
- Le matériel doit être acheté pour le démarrage et la maintenance.
- Les organisations disposent d’un contrôle total sur les ressources et la sécurité.
- Les organisations sont responsables de la maintenance et des mises à jour du matériel.
Cloud hybride
- Offre la plus grande flexibilité.
- Les organisations déterminent où exécuter leurs applications.
- Les organisations contrôlent la sécurité, la conformité ou les exigences légales.
Consumption-based model
Capital expenditure (CapEx) : buy material, once paid is yours, but limited resources.
Operational expenditure (OpEx): rent material, public cloud consumption-based model: You’re billed only for what you use.
Summary
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/security/fundamentals/shared-responsibility
High Availability - SLAS

Scaling
Vertical scaling is focused on increasing or decreasing the capabilities of resources. Horizontal scaling is adding or subtracting the number of resources.
IaaS
Maximum of control on the resources. IaaS helps you reduce the cost and complexity of maintaining a physical server and its datacenter infrastructure. Virtual networks are part of the IaaS cloud service.
Describe different cloud services - Training | Microsoft Learn
PaaS
PaaS is well suited to provide a complete development environment without the headache of maintaining all the development infrastructure.
In PaaS, the cloud provider is responsible for the operating system, physical datacenter, physical hosts, and physical network. In PaaS, the customer is responsible for accounts and identities.
Describe different cloud services - Training | Microsoft Learn
SaaS
Typical for enterprises services like ERP
SaaS is software that is centrally hosted and managed for you and your users or customers. Usually, one version of the application is used for all customers, and it is licensed through a monthly or annual subscription. PaaS and IaaS use a consumption-based model, so you only pay for what you use.
Describe different cloud services - Training | Microsoft Learn
2 Learning Path: Azure compute and networking services
Virtual machines
VMs are an ideal choice when you need:
- Total control over the operating system (OS).
- The ability to run custom software.
- To use custom hosting configurations.
VM Resources:
- Size (purpose, number of processor cores, and amount of RAM)
- Storage disks (hard disk drives, solid state drives, etc.)
- Networking (virtual network, public IP address, and port configuration)
Azure Reservations offers discounted prices on certain Azure services. Azure Reservations can save you up to 72 percent compared to pay-as-you-go prices. To receive a discount, you can reserve services and resources by paying in advance.
Spending limits can suspend a subscription when the spend limit is reached.
Manage and minimize total cost on Azure - Training | Microsoft Learn
Virtual machine scale sets (VMSS)
Large-scale services for areas such as compute, big data, and container workloads.
Automatically deploy a load balancer.
Virtual machine scale enables you to provision a group of matching and load-balanced virtual machines in Azure.
Imagine you are running a website that enables scientists to upload astronomy images that need to be processed. If you duplicated the VM, you would normally need to configure an additional service to route requests between multiple instances of the website. Virtual machine scale sets could do that work for you.
Virtual machine availability sets (VMAS)
Availability sets are designed to ensure that VMs stagger updates and have varied power and network connectivity, preventing you from losing all your VMs with a single network or power failure.
Group by “update domain” (VMs that can be rebooted at the same time) or “fault domain” (VMs by common power source and network switch).
Differences between VMSS and VMAS: https://www.c-sharpcorner.com/Blogs/differentiate-between-availability-set-availability-zone-and-scale-set
Azure Batch
Azure Batch enables large-scale parallel and high-performance computing (HPC) batch jobs with the ability to scale to tens, hundreds, or thousands of VMs.
Source: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/training/modules/azure-compute-fundamentals/azure-virtual-machines
Azure Virtual Desktop
Desktop and application virtualization service that runs on the cloud.
Centralized security management for users’ desktops with Azure Active Directory.
Azure Containers
Azure Container Instances: platform as a service (PaaS) offering allow you to upload your containers and run the containers.
Azure Functions
Concerned about the code and not about the infrastructure.
Good choice when demand is variable.
Only charged for the CPU time used while your function runs.
Stateless by default, Stateful called “Durable Functions” a context is passed.
Azure App Service
Host most common app service styles like:
- Web apps (hosting ASP.NET, ASP.NET Core, Java, Ruby, Node.js, PHP, or Python)
- API apps (REST-based web APIs )
- WebJobs (scheduled or run by a trigger)
- Mobile apps (back end for iOS and Android apps)
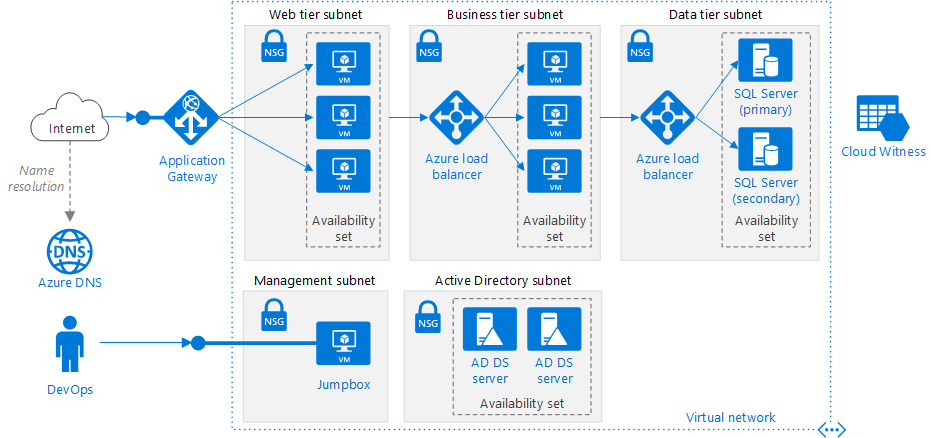
Azure Virtual Network
Azure virtual networks provide the following key networking capabilities:
- Isolation and segmentation
- Internet communications
- Communicate between Azure resources
- Communicate with on-premises resources
- Route network traffic
- Filter network traffic
- Connect virtual networks
Peering can connect Vnets: 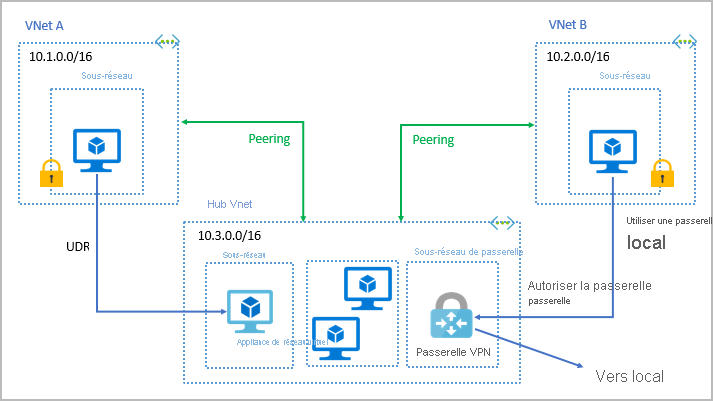
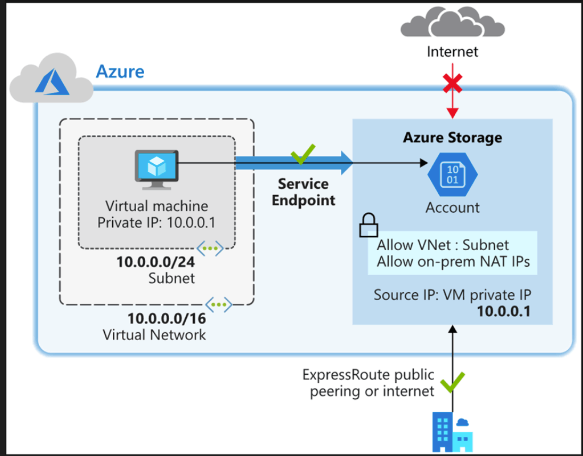
Azure Service endpoints
Service endpoints are used to expose Azure services to a virtual network, providing communication between the two. ExpressRoute is used to connect an on-premises network to Azure. NSGs allow you to configure inbound and outbound rules for virtual networks and virtual machines. Peering allows you to connect virtual networks together.
Azure Virtual Network fundamentals - Training | Microsoft Learn
VPN gateways
A VPN gateway is a type of virtual network gateway. Azure VPN Gateway instances are deployed in a dedicated subnet of the virtual network and enable the following connectivity:
- Connect on-premises datacenters to virtual networks through a site-to-site connection.
- Connect individual devices to virtual networks through a point-to-site connection.
- Connect virtual networks to other virtual networks through a network-to-network connection.
Site-to-site VPN: Established between on-premises VPN device and an Azure VPN Gateway that is deployed in a virtual network. This connection type allow communication between any on-premises authorize resource to access a virtual network through an encrypted tunnel.
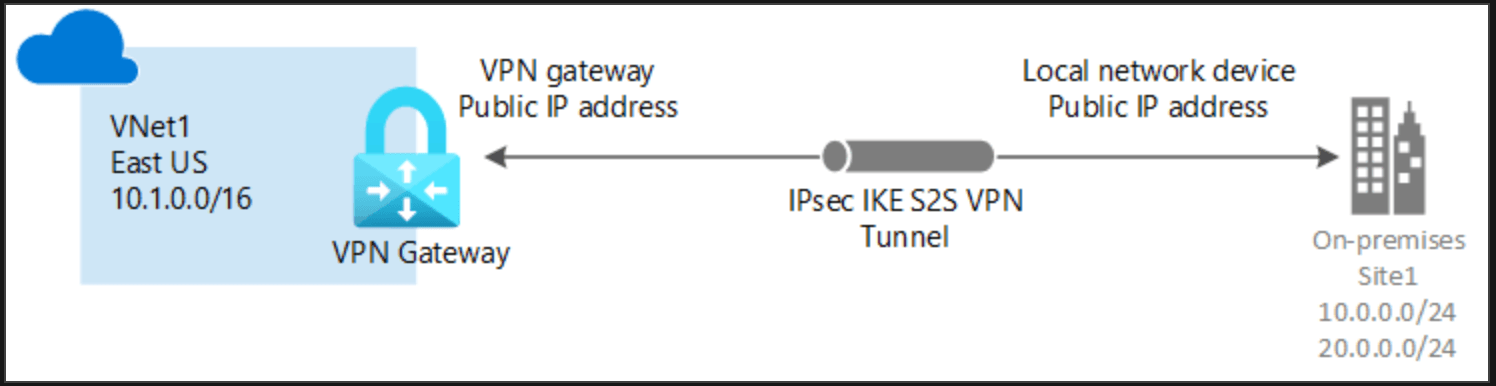
Point-to-site: A Point-to-Site (P2S) VPN gateway connection lets you create a secure connection to your virtual network from an individual client computer.
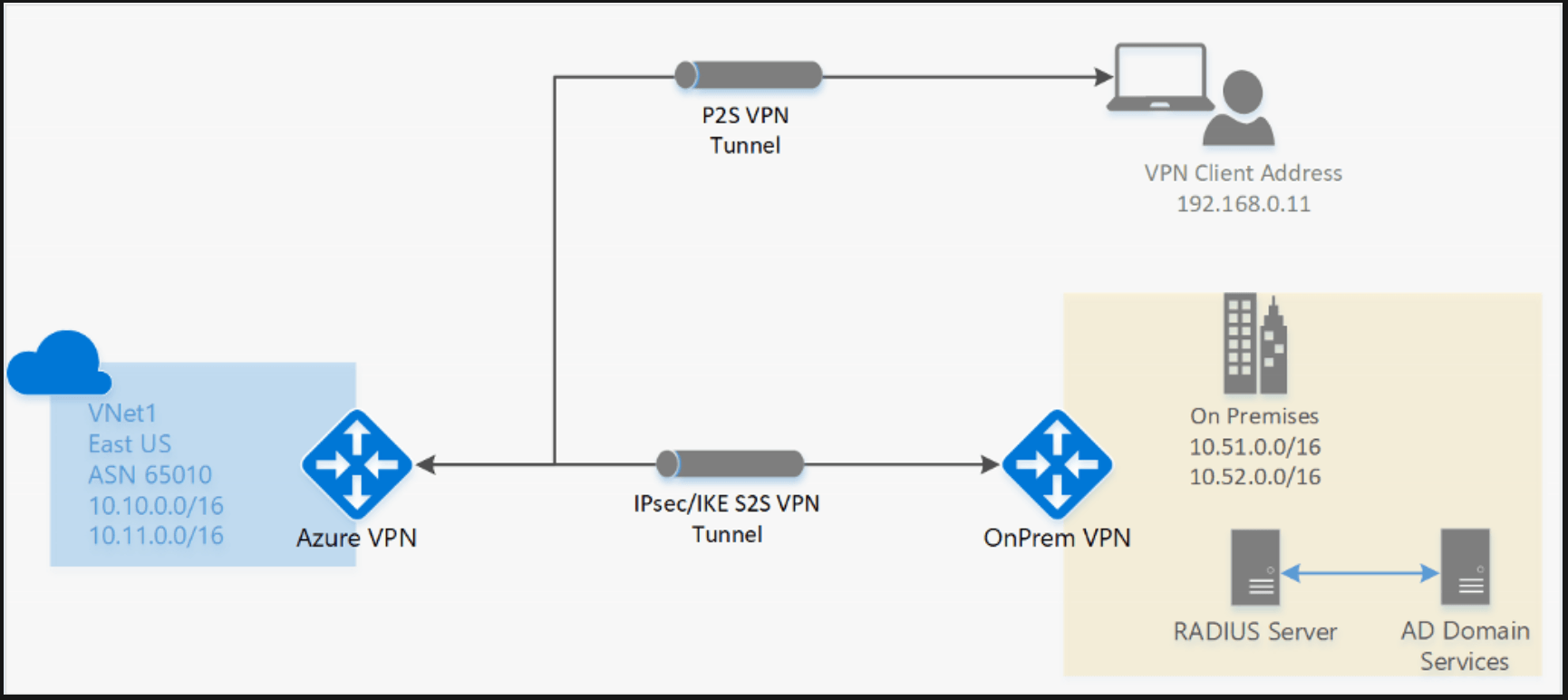
Source: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/vpn-gateway/point-to-site-about
Azure ExpressRoute
Azure ExpressRoute lets you extend your on-premises networks into the Microsoft cloud over a private connection, with the help of a connectivity provider.
ExpressRoute provides direct connectivity to Azure cloud services and connects Microsoft’s global network. All transferred data is not encrypted, and do not go over the public Internet.
VPN Gateway provides secured connectivity to Azure cloud services over the public Internet. All transferred data is encrypted in a private tunnel as it crosses the internet.
A Point-to-point Ethernet connection is supported by ExpressRoute for connecting your on-premises network to Azure.
The three models that ExpressRoute supports are:
- CloudExchange colocation
- Point-to-point Ethernet connection
- Any-to-any-connection
ExpressRoute connections and Azure VPN Gateway are two services that you can use to connect an on-premises network to Azure. Bastion provides a web interface to remotely administer Azure virtual machines by using SSH/RDP. Azure Firewall is a stateful firewall service used to protect virtual networks.
Azure ExpressRoute: Connectivity models | Microsoft Learn
Azure VPN Gateway fundamentals - Training | Microsoft Learn
Azure DNS
- manage DNS records
- supports private DNS domains
- supports alias record sets
Azure Storage
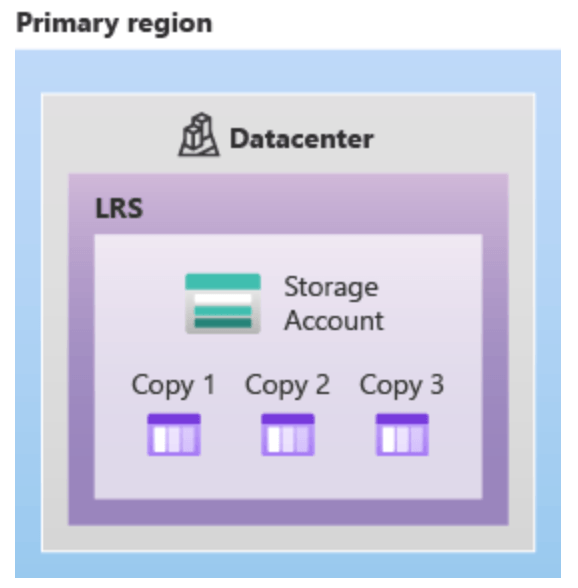
Locally redundant storage (LRS): redondance sur le même DC (le plus simple, pas cher)
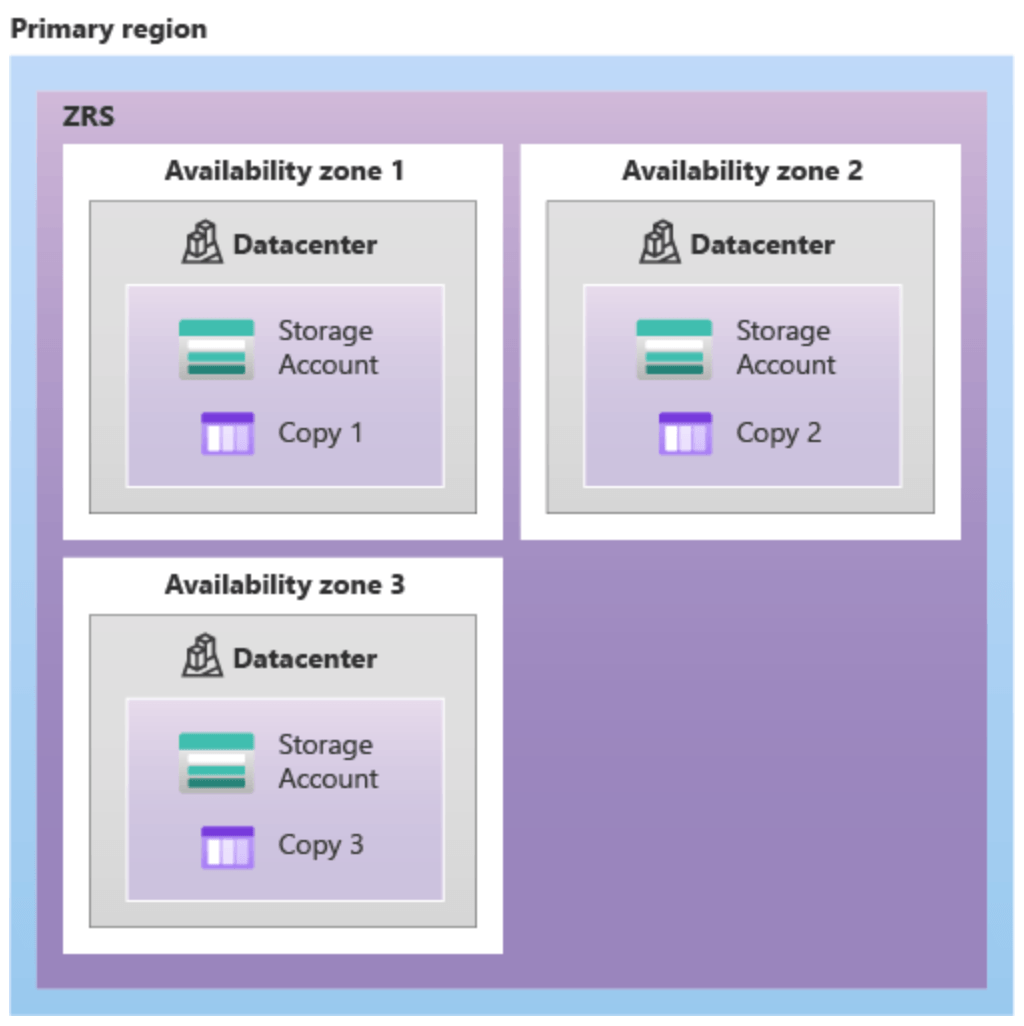
Zone-redundant storage (ZRS): redondance sur plusieurs zone/DC (HA et gouvernance)
Geo-redundant storage (GRS): redondance locale ET dans un autre DC/zone
Geo-redundant storage (GRS) -Replicates your data to a secondary region that is in different geographic locations from the primary region.
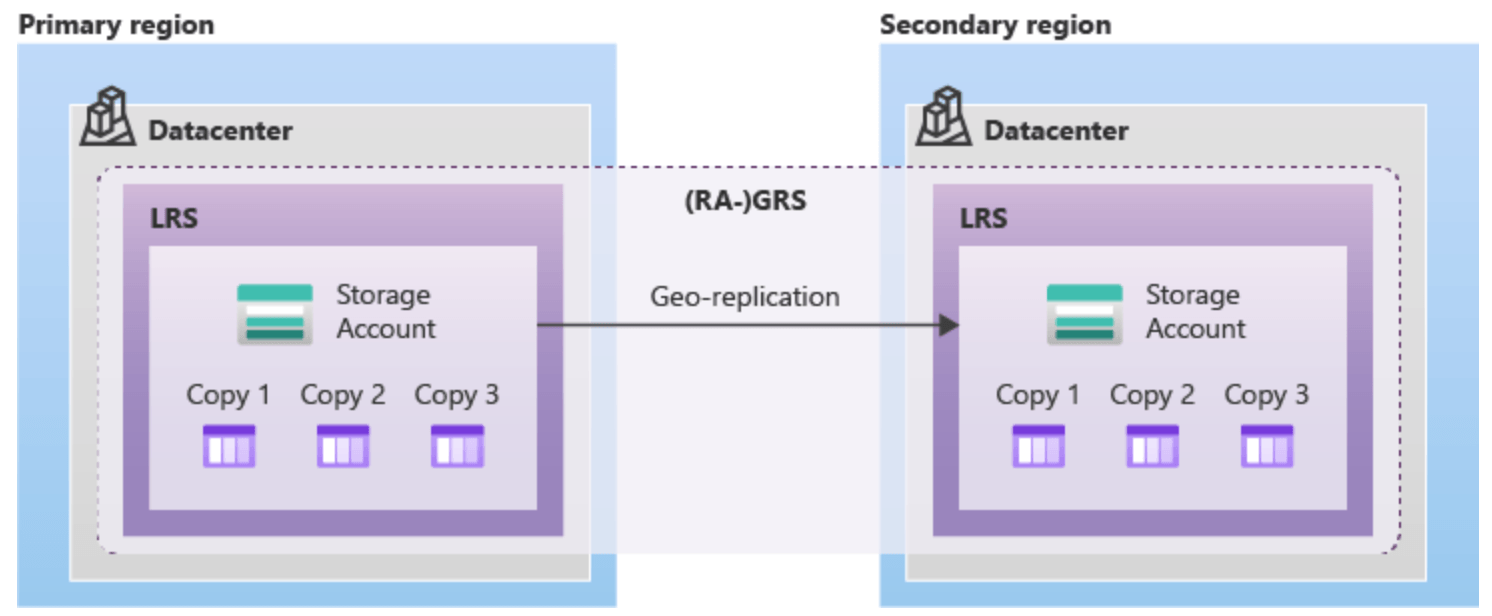
Geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS): redondance sur plusieurs zones/DC ET redondance dans un autre DC (top)
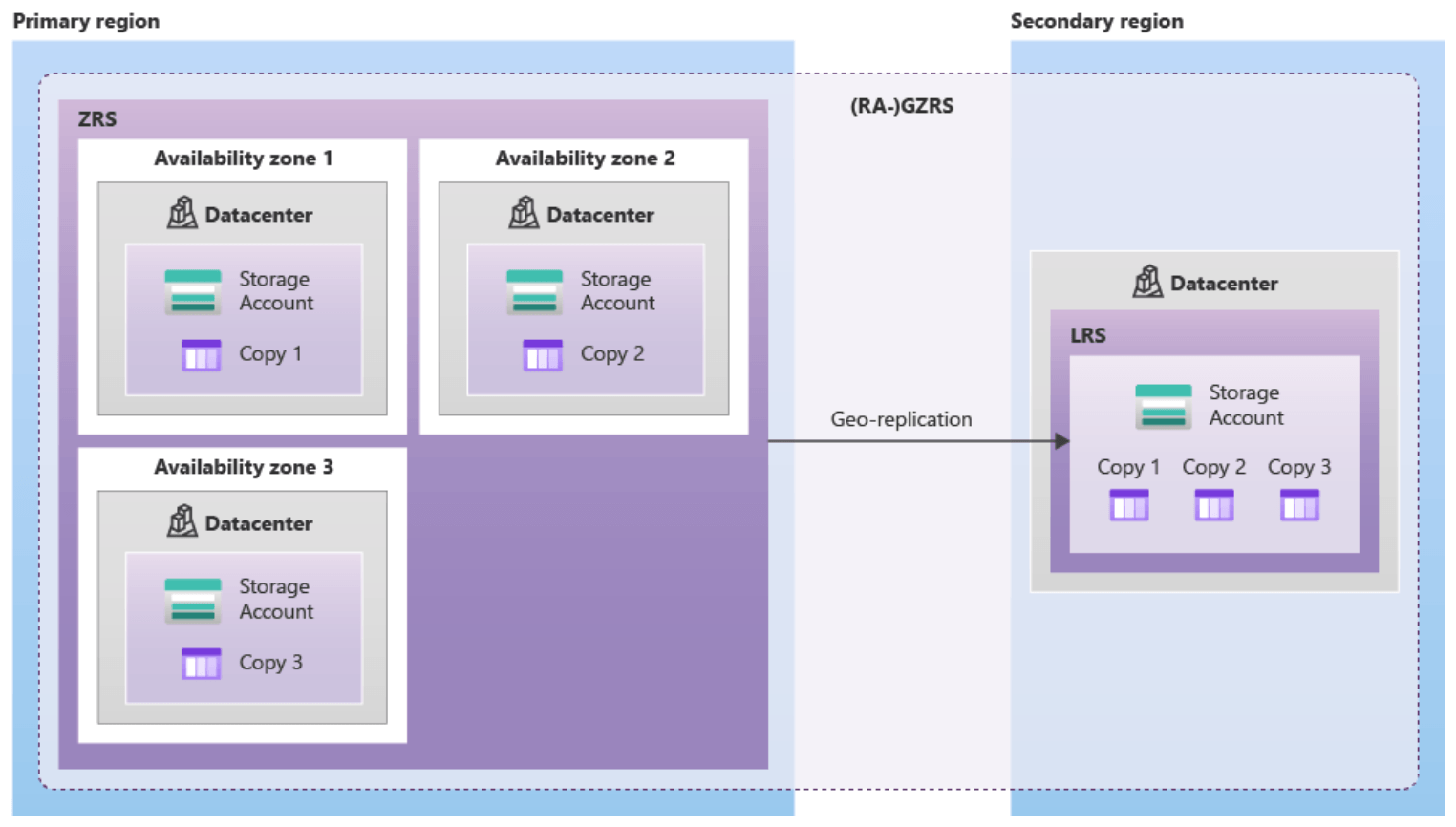
Reference: https://gudurustechblog.wordpress.com/2021/09/15/azure-storage-redundancy/
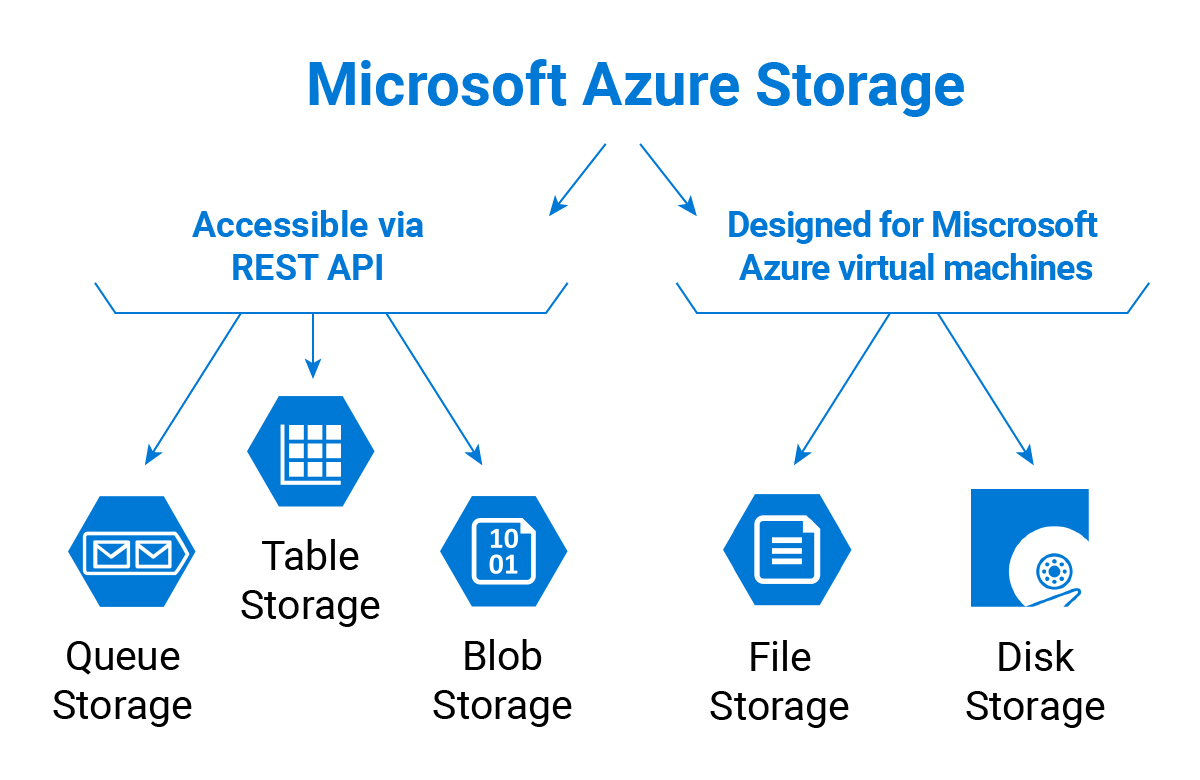
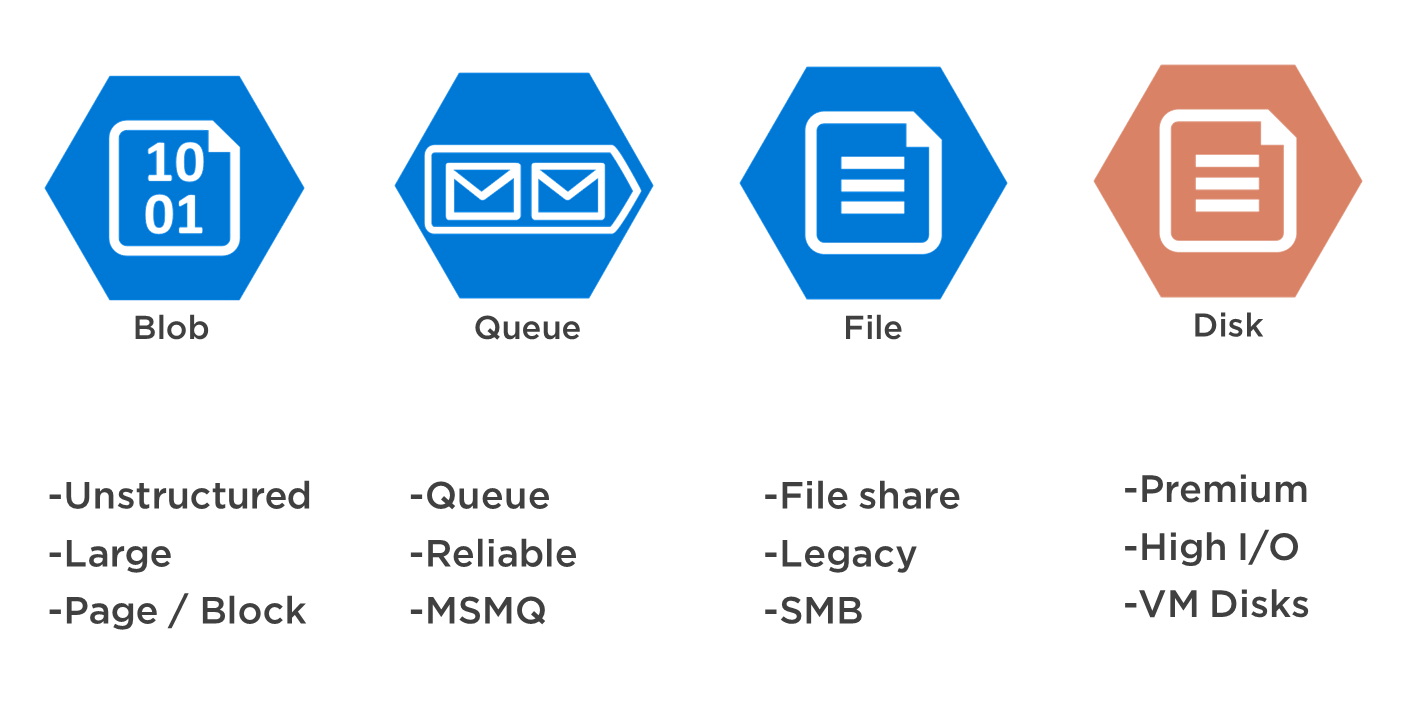
The Azure Storage platform includes the following data services:
- Azure Blobs: A massively scalable object store for text and binary data. Also includes support for big data analytics through Data Lake Storage Gen2.
- Azure Files: Managed file shares for cloud or on-premises deployments.
- Azure Queues: A messaging store for reliable messaging between application components.
- Azure Disks: Block-level storage volumes for Azure VMs.
Geo-distribution:
Because of geo-distribution you can deploy apps and data to regional datacenters around the globe, thereby ensuring that your customers always have the best performance in their region.
Azure Storage
Azure Blob storage
Azure Blob storage is an object storage solution that you can use to store massive amounts of unstructured data, such as text or binary data.
Azure Storage account fundamentals - Training | Microsoft Learn
Identity
Azure AD: authentification, sso, gestion apps et devices
Azure AD Connect synchronise les identités utilisateur entre un Active Directory local et Azure AD.
Active Directory Domain Services: domain join, group policy, LDAP, and Kerberos/NTLM authentication.
Authentication: standard passwords, single sign-on (SSO), multifactor authentication (MFA), and passwordless
Authentication - To confirm the identity of a person who wants access.
Authentication is the process of establishing the identity of a person or service that wants to access a resource.
Authorization - To grant the proper access to a legitimate user.
Authorization is the process of establishing what level of access a legitimate user or service should have.
Conditional Access
Conditional Access is a tool that Azure AD uses to allow or deny access to resources based on identity signals, such as the device being used. SSO enables a user to sign in one time and use that credential to access multiple resources and applications from different providers. MFA is a process whereby a user is prompted during the sign-in process for an additional form of identification. Hybrid identity solutions create a common user identity for authentication and authorization to all resources, regardless of location.
Conditional Access can use signals to determine information about authentication attempts, and then determine whether to block access or require additional verifications, such as MFA.
What are multifactor authentication and Conditional Access? - Training | Microsoft Learn
Azure AD provides services for verifying identity and access to applications and resources. SSO enables you to remember a single username and password to access multiple applications and is available in Azure AD.
What is Azure Active Directory? - Training | Microsoft Learn
Azure accounts
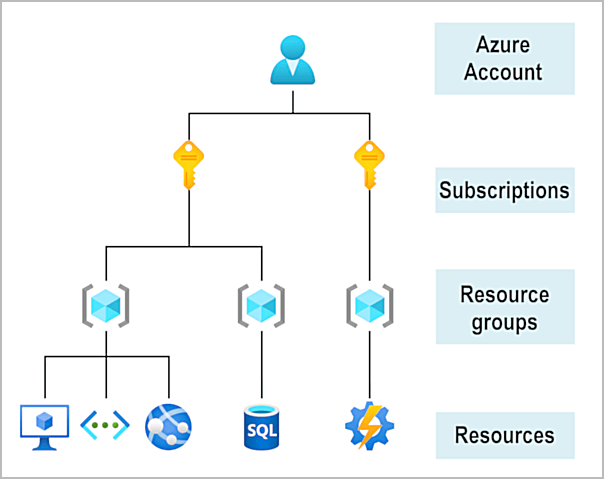
Free account: 12 months access to certain services, 200$ the first 30 days, 25 free services
Student account: 12 months access to certain services, 200$ the first 12 month, free dev tools
Learn sandbox: temp subscription to do exercices
Azure generates separate billing reports and invoices for each subscription so that you can organize and manage costs. Resource groups can be used to group costs, but you will not receive a separate invoice for each resource group. Management groups are used to efficiently manage access, policies, and compliance for subscriptions. You can set up billing profiles to roll up subscriptions into invoice sections, but this requires customization.
Azure subscriptions and management groups - Training | Microsoft Learn
Management groups
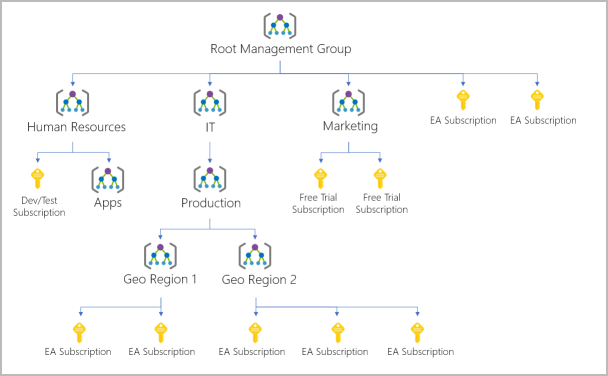
Management groups help you manage access, policy, and compliance for multiple subscriptions. All subscriptions in a management group automatically inherit the conditions applied to the management group.
Azure DC, Region, AZ
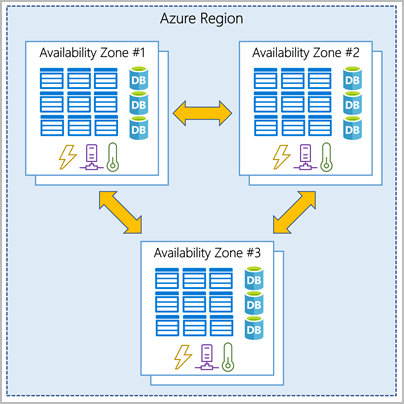 AZ: 1 or more DC
AZ: 1 or more DC
- Zonal services: You pin the resource to a specific zone (for example, VMs, managed disks, IP addresses).
- Zone-redundant services: The platform replicates automatically across zones (for example, zone-redundant storage, SQL Database).
- Non-regional services: Services are always available from Azure geographies and are resilient to zone-wide outages as well as region-wide outages.
Availability zones are physically separate datacenters within an Azure region. Each availability zone is made up of one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking.
Azure regions, availability zones, and region pairs - Training | Microsoft Learn
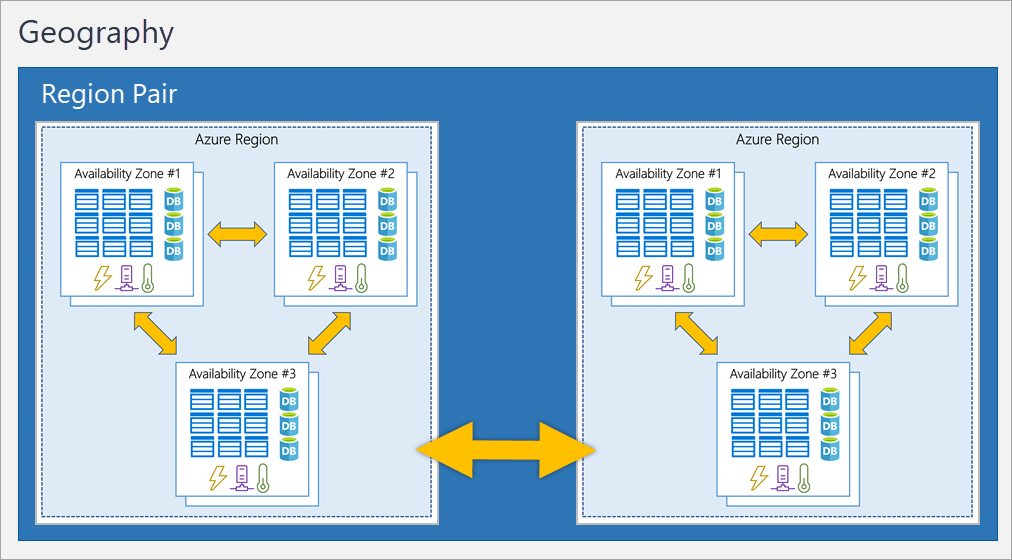
Region pairs allow the replication of Azure resources across geographies to help ensure that a secondary region is available in case of any disaster at the primary region.
Azure regions, availability zones, and region pairs - Training | Microsoft Learn
Layers of defense in depth
A defense in depth strategy uses a series of mechanisms to slow the advancement of an attack that aims to gain unauthorized access to data. The principle of least privilege means restricting access to information to only the level that users need to perform their work. A DDoS attack attempts to overwhelm and exhaust an application’s resources. The perimeter layer is about protecting an organization’s resources from network-based attacks.
What is defense in depth? - Training | Microsoft Learn
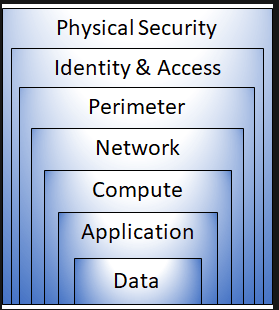
- The physical security layer is the first line of defense to protect computing hardware in the datacenter.
- The identity and access layer controls access to infrastructure and change control.
- The perimeter layer uses distributed denial of service (DDoS) protection to filter large-scale attacks before they can cause a denial of service for users.
- The network layer limits communication between resources through segmentation and access controls.
- The compute layer secures access to virtual machines.
- The application layer helps ensure that applications are secure and free of security vulnerabilities.
- The data layer controls access to business and customer data that you need to protect.
3 Learning Path: Describe Azure management and governance
Azure Resource Manager
ARM is the deployment and management service for Azure. It provides a management layer that enables you to create, update, and delete resources in an Azure subscription. You use management features, such as access control, resource locks, and resource tags, to secure and organize resources after deployment.
Azure resources and Azure Resource Manager - Training | Microsoft Learn
Azure blueprints
Azure Blueprints provide a way to define a repeatable set of Azure resources. Azure Blueprints enable development teams to rapidly provision and run new environments, with the knowledge that they’re in line with the organization’s compliance requirements. Teams can also provide Azure resources across several subscriptions simultaneously, meaning they can achieve shorter development times and quicker delivery.
By using ARM templates, you can describe the resources you want to use in a declarative JSON format.
Identify the product options - Training | Microsoft Learn
Azure policies
Ensure resources are compliant.
Azure Policy is designed to help enforce standards and assess compliance across your organization. Through its compliance dashboard, you can access an aggregated view to help evaluate the overall state of the environment. You can drill down to a per-resource, or per-policy level granularity. You can also use capabilities like bulk remediation for existing resources and automatic remediation for new resources, to resolve issues rapidly and effectively
Azure Locks
Prevent resources modification.
Resource locks can be used to prevent resources from being accidentally deleted or changed. Even with role-based access control policies in place there is still a risk that people with the right level of access could delete a critical resource. Azure Resource Manager locks prevent users from accidentally deleting or modifying a critical resource, and can be applied to a subscription, a resource group, or a resource.
Service Trust Portal
https://servicetrust.microsoft.com/
Azure ARC
- Serveurs
- Clusters Kubernetes
- Services de données Azure
- SQL Server
- Machines virtuelles (préversion)
Azure Advisor
- Reliability is used to ensure and improve the continuity of your business-critical applications.
- Security is used to detect threats and vulnerabilities that might lead to security breaches.
- Performance is used to improve the speed of your applications.
- Operational Excellence is used to help you achieve process and workflow efficiency, resource manageability, and deployment best practices.
- Cost is used to optimize and reduce your overall Azure spending.
Azure Health
- Azure Status is a global view of the health of all Azure services across all Azure regions.
- Service Health: the Azure services and regions you’re using. Azure Service Health alerts you about service issues that happen in Azure itself, such as a regional Azure outage
- Resource Health is a tailored view of your actual Azure resources.
Source: https://learn.microsoft.com/training/modules/monitoring-fundamentals/2-identify-product-options
After an outage, Service Health provides official incident reports called root cause analysis (RCA), which you can share with stakeholders.
Identify your product options - Training | Microsoft Learn
Azure Monitor
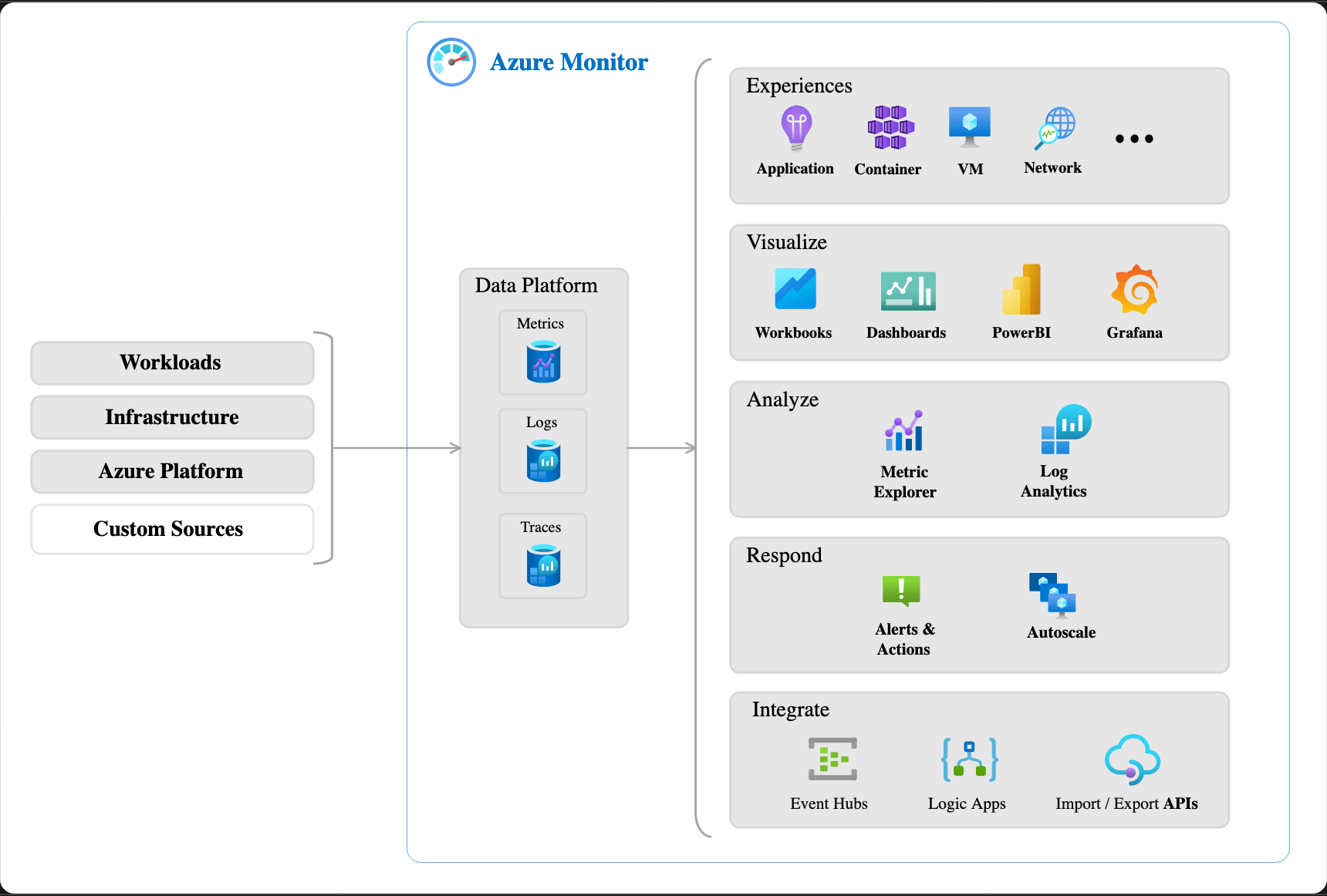
Application Insights: monitor our web applications
Application Insights is a feature of Azure Monitor that allows you to monitor running applications, automatically detect performance anomalies, and use built-in analytics tools to see what users do on an app.
Identify your product options - Training | Microsoft Learn
Health advisories
Health advisories are issues that require that you take proactive action to avoid service interruptions, such as service retirements and breaking changes. Service issues are problems such as outages that require immediate actions.
Identify your product options - Training | Microsoft Learn
Costs
Pricing calculator: https://azure.microsoft.com/fr-fr/pricing/calculator/
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership): https://azure.microsoft.com/fr-fr/pricing/tco/calculator/
Pour calculer le coût d’économie dans le cloud Azure
Tags
Resource management Tags:
- enable you to locate and act on resources that are associated with specific workloads, environments, business units, and owners.
Cost management and optimization Tags:
- enable you to group resources so that you can report on costs, allocate internal cost centers, track budgets, and forecast estimated cost.
Operations management Tags:
- enable you to group resources according to how critical their availability is to your business. This grouping helps you formulate service-level agreements (SLAs). An SLA is an uptime or performance guarantee between you and your users.
Security Tags:
- enable you to classify data by its security level, such as public or confidential.
Governance and regulatory compliance Tags:
- enable you to identify resources that align with governance or regulatory compliance requirements, such as ISO 27001.
- Tags can also be part of your standards enforcement efforts. For example, you might require that all resources be tagged with an owner or department name.
Workload optimization and automation Tags:
- can help you visualize all of the resources that participate in complex deployments. For example, you might tag a resource with its associated workload or application name and use software such as Azure DevOps to perform automated tasks on those resources.
Example:
A resource tag consists of a name and a value. You can assign one or more tags to each Azure resource.
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| AppName | The name of the application that the resource is part of. |
| CostCenter | The internal cost center code. |
| Owner | The name of the business owner who’s responsible for the resource. |
| Environment | An environment name, such as “Prod,” “Dev,” or “Test.” |
| Impact | How important the resource is to business operations, such as “Mission-critical,” “High-impact,” or “Low-impact.” |